March 21, 2025
The AI Revolution Needs Encryption—Here’s Why It Matters
In the age of artificial intelligence (AI), data serves as the lifeblood of innovation. However, the sheer scale and sensitivity of data used in AI systems make it a prime target for breaches, misuse, and regulatory scrutiny. Data encryption has emerged as a cornerstone of safeguarding AI processes, offering robust solutions to challenges like data security in case of leaks and traceability for compliance.
Understanding Data Encryption
At its core, data encryption transforms readable data into an encoded format that can only be accessed with the appropriate decryption key. By making information unreadable to unauthorized users, encryption acts as a critical defense layer against unauthorized access, ensuring that sensitive data remains secure even in the event of a breach. In the context of AI training and algorithm usage, encryption plays a pivotal role at multiple stages—from data collection to storage and processing.
Limiting Data Access to Prevent Leaks
One of the most significant concerns in AI is the potential for data leaks. The datasets used to train AI models often contain sensitive information, including personally identifiable information (PII), proprietary business data, or confidential medical records. A breach could have catastrophic consequences, ranging from legal repercussions to reputational damage.
Data encryption mitigates these risks by ensuring that only precisely identified information is shared with the AI training algorithm. In an encrypted data lake, data is inaccessible by default and must be explicitly shared with the AI engine to be utilized. This means that the data that is made available to the AI engine can be set to access only anonymous data.
Enhancing Data Traceability for Compliance
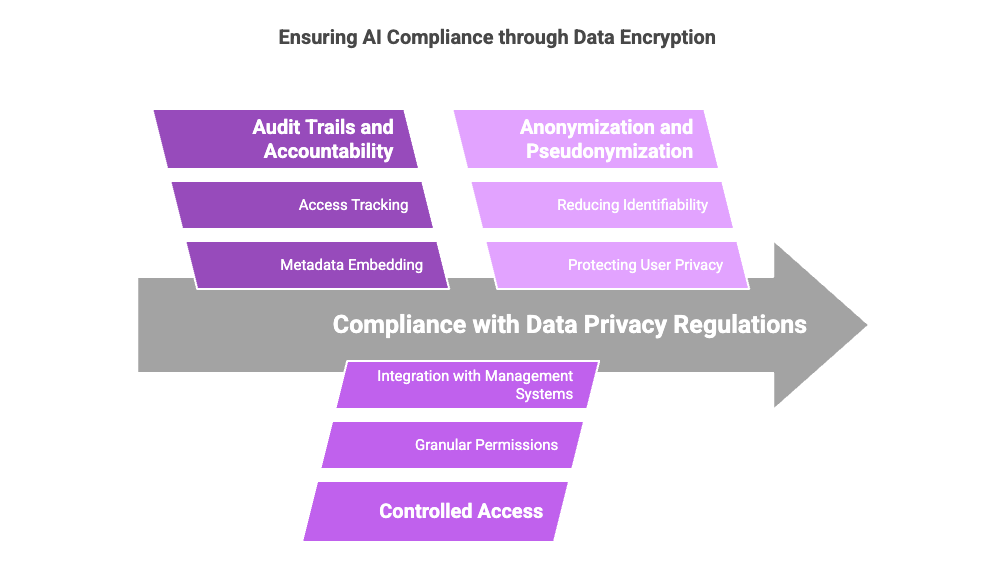
AI systems are subject to increasing scrutiny from regulators and watchdogs concerned about data privacy and ethical usage. Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) mandate stringent controls over how data is collected, stored, and processed. Data encryption supports compliance in several ways:
-
Audit Trails and Accountability: Encryption tools can embed metadata and unique identifiers into datasets, enabling organizations to track who accessed the data, when, and for what purpose. This traceability fosters accountability and simplifies compliance reporting.
-
Controlled Access: Encryption allows for granular control over who can access specific datasets. By integrating encryption with access management systems, organizations can ensure that only authorized individuals or algorithms can use the data.
-
Anonymization and Pseudonymization: Encrypting data enables organizations to anonymize or pseudo-anonymize sensitive information, reducing the risk of exposure while still allowing AI models to extract meaningful insights.
Enabling Collaboration Without Compromising Privacy
Collaboration is a key driver of innovation in AI. Researchers and organizations often need to share data to build more robust models or tackle complex problems. However, sharing sensitive data can expose it to security risks. Encryption bridges this gap by enabling secure collaboration:
-
Homomorphic Encryption: This advanced encryption method allows AI models to process encrypted data without decrypting it. As a result, organizations can collaborate on data-intensive projects without exposing raw datasets.
-
Secure Multi-Party Computation: Encryption facilitates scenarios where multiple parties can jointly compute AI models on shared datasets without revealing their individual data inputs.
Building Trust with Stakeholders
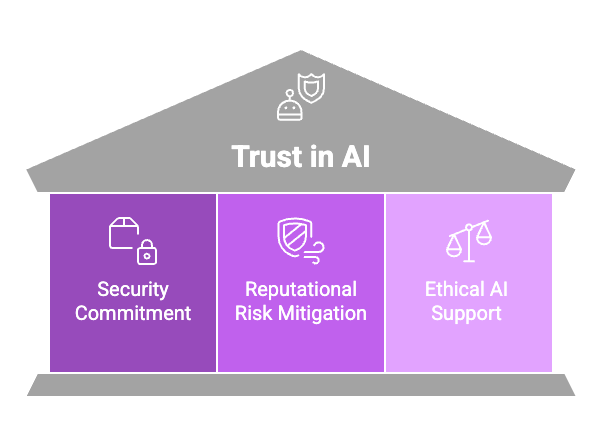
Trust is essential for the widespread adoption of AI. Users, regulators, and business partners need assurance that their data will be handled responsibly. Encryption plays a crucial role in building this trust by:
Demonstrating a Commitment to Security: Organizations that prioritize encryption signal their dedication to safeguarding stakeholder data.
-
Mitigating Reputational Risks: In the event of a breach, encrypted data is significantly less damaging than unprotected information, helping to preserve trust and reputation.
-
Supporting Ethical AI Development: Encryption aligns with the ethical principles of transparency, accountability, and fairness by ensuring that data privacy is a top priority.
Enabling Compliance with Data Localization Requirements
Many countries enforce data localization or data residency laws, requiring organizations to store and process data within their borders. Encryption simplifies compliance with these regulations by:
-
Securing Cross-Border Transfers: When data needs to move across jurisdictions, encryption ensures that it remains secure and compliant with local laws.
-
Protecting Localized Data: Encrypting data stored in-country adds an extra layer of protection against local threats.
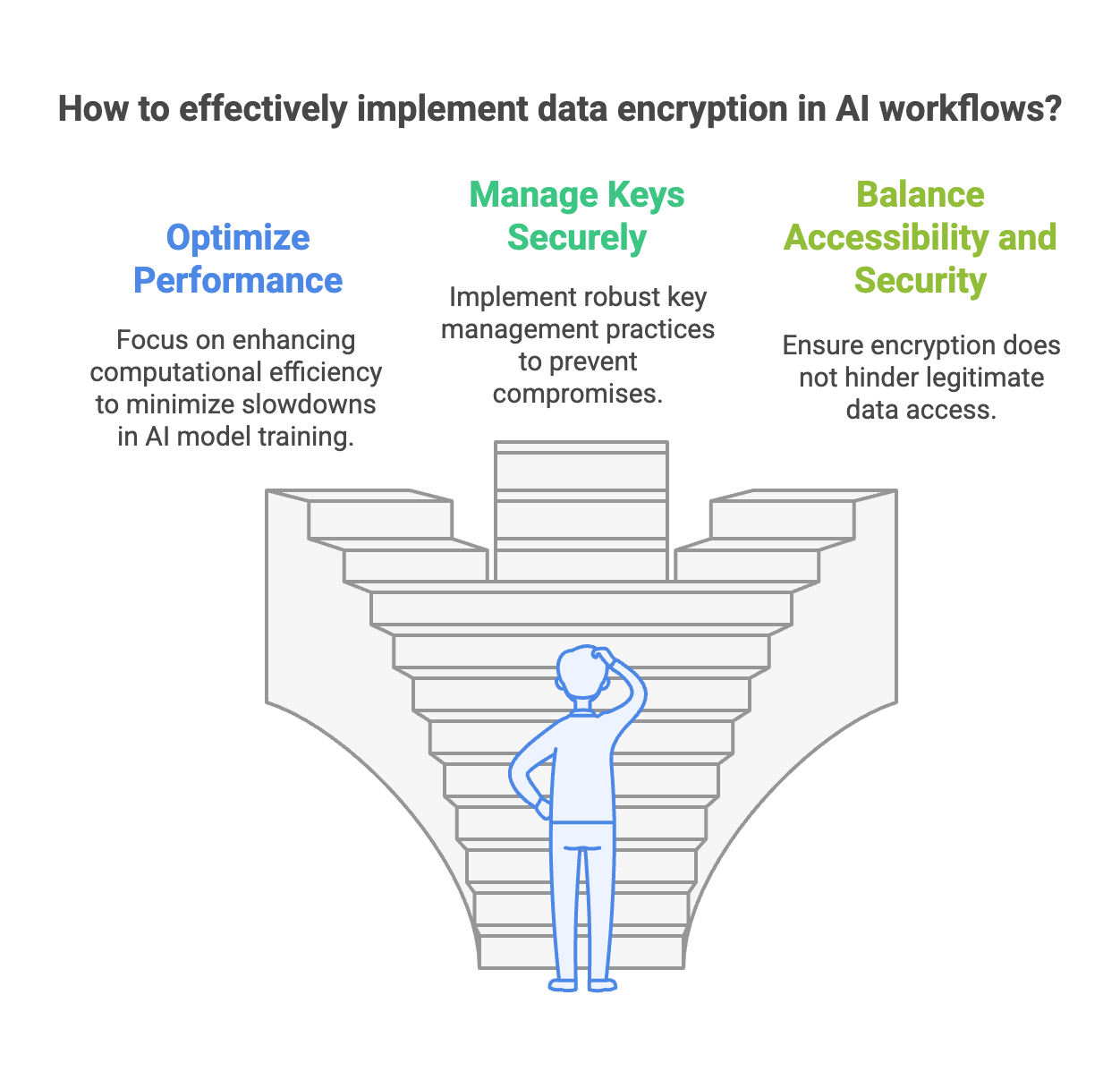
Challenges and Best Practices for Encryption in AI
While the benefits of data encryption are clear, implementing it effectively in AI workflows comes with challenges:
-
Performance Overheads: Encrypting and decrypting data can increase computational requirements, potentially slowing down AI model training. Organizations can address this by optimizing encryption algorithms and leveraging specialized hardware.
-
Key Management: Protecting encryption keys is critical, as compromised keys can render encryption useless. Best practices include using hardware security modules (HSMs) and key rotation policies.
-
Balancing Accessibility and Security: Ensuring that encryption doesn’t hinder legitimate access to data requires careful planning and integration with access management systems.
The Future of Encryption in AI
As AI continues to evolve, so too will the methods for protecting data. Emerging technologies like quantum-resistant encryption and advanced homomorphic encryption are set to revolutionize data security. These innovations promise to address current limitations and provide even greater assurances of privacy and security.
Moreover, the integration of encryption with AI-specific frameworks will likely become standard practice. Organizations that adopt encryption early and proactively will be better positioned to navigate the complex landscape of data security, compliance, and ethical AI development.
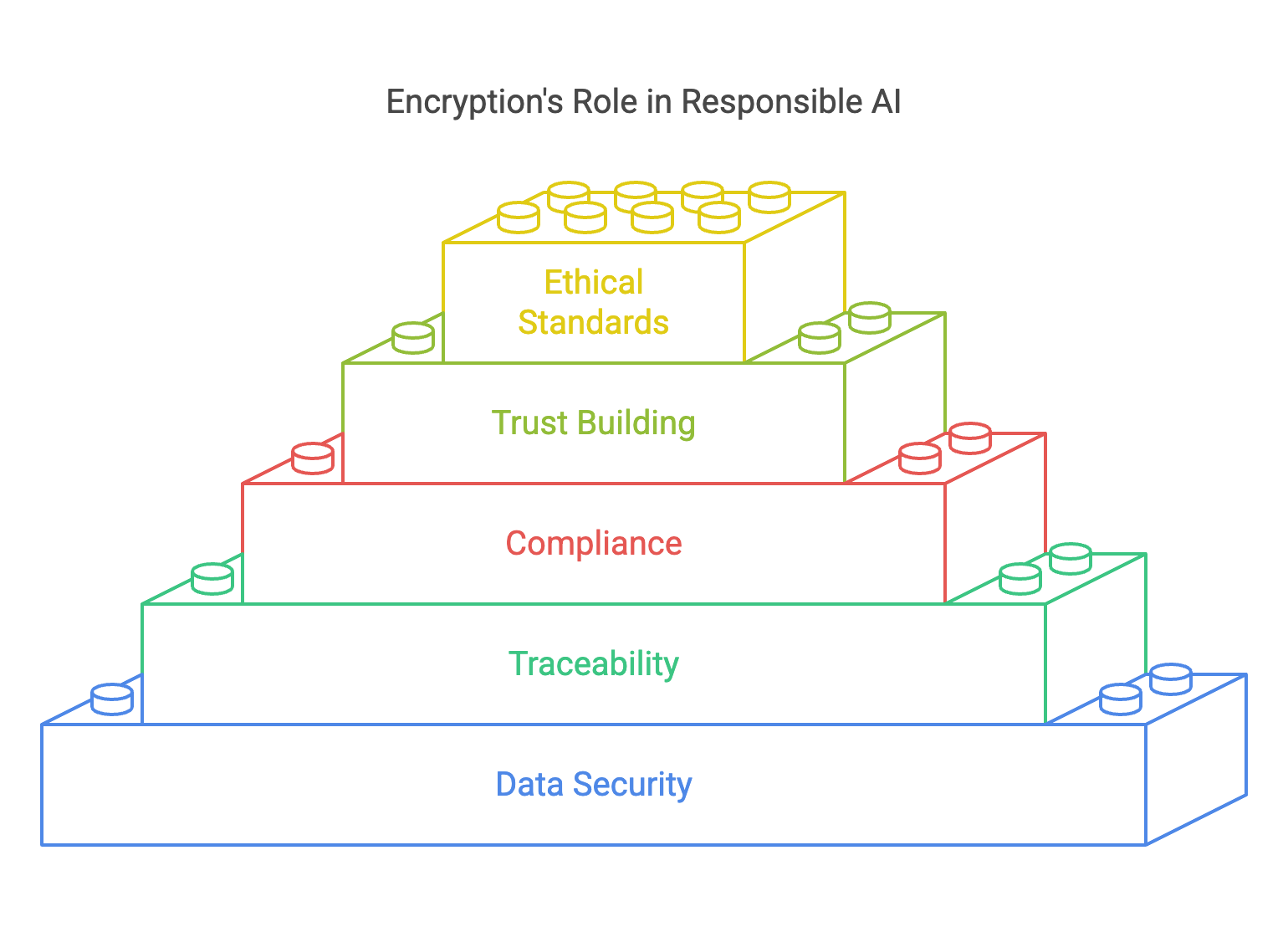
Conclusion
Data encryption is more than just a security measure
It is a fundamental enabler of responsible and effective AI. By protecting sensitive information, ensuring traceability, and fostering trust, encryption empowers organizations to harness the full potential of AI while safeguarding the interests of individuals and stakeholders. As the AI landscape and more generally data security regulations grow increasingly complex, investing in robust encryption practices will be essential for driving innovation, maintaining compliance, and upholding ethical standards in a data-driven world.
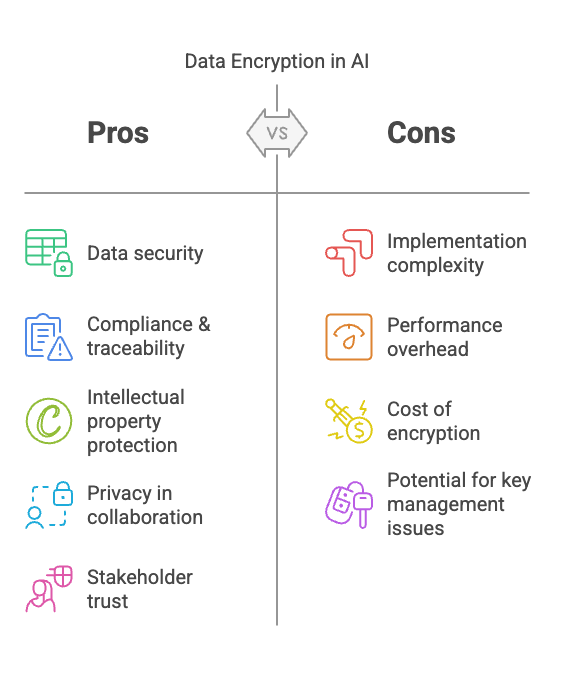
Summary of the Pros & Cons of Data Encryption
At iCure we’ve been working hard to make sure Cardinal Backend & SDK’s take care of the implementation and key management complexity, optimizes performances and enable you to seamlessly access all data encryption’s benefits.
Medical records of more than 4mio patients are already encrypted and securely accessed by authorized doctors, patients and scientists thanks to iCure technology.
Visit us: https://icure.com
Start developing: https://cardinalsdk.com
Created with AI – reviewed & improved by humans. Copyright iCure 2025

